As the power and operating frequency of electronic devices continue to increase, heat dissipation has become a critical factor affecting performance and lifespan. In the field of thermal management, thermal conductive gel and thermally conductive potting compound are two commonly used solutions, each widely applied in various electronic devices. Although both materials provide thermal conductivity, they differ significantly in material characteristics, application scenarios, and functionality. This article will delve into the differences between thermal conductive gel and thermally conductive potting compound to help professionals select the most suitable thermal material based on their specific needs.
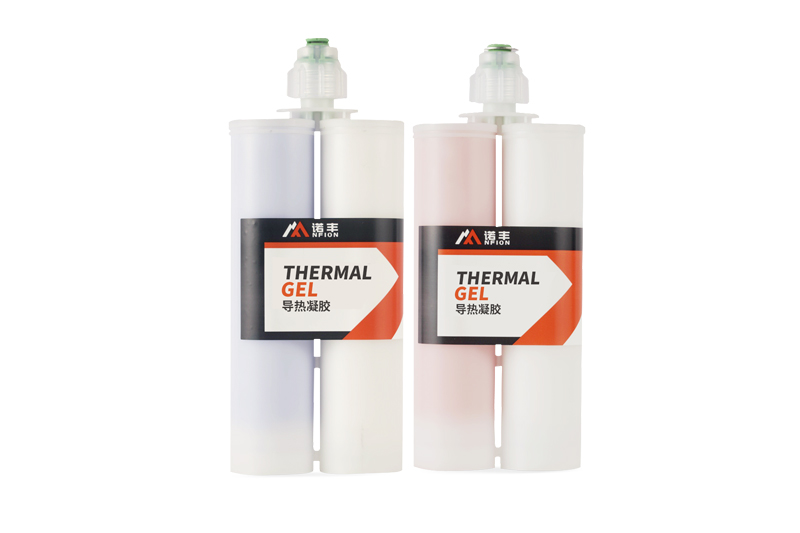

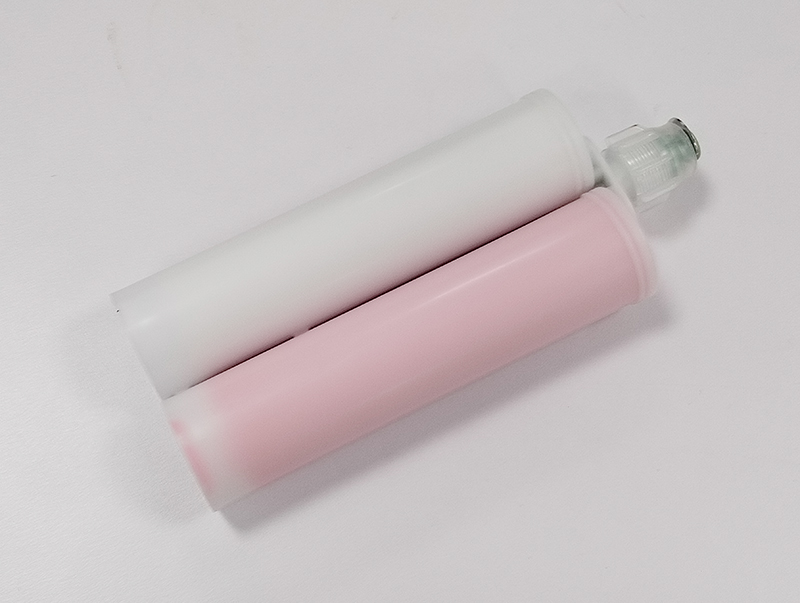
Characteristics:
● High Flexibility: Thermal conductive gel remains somewhat soft after curing, suitable for electronic devices that experience mechanical vibrations or thermal expansion.
● Low Stress Application: Due to its softness, thermal conductive gel does not exert excessive mechanical stress on components during application, helping to protect sensitive electronic parts.
Application Scenarios:
Thermal conductive gel is mainly used in electronic devices requiring frequent maintenance, replacement, or disassembly, such as communication equipment, data center servers, automotive electronics, and battery management systems. It provides an effective heat dissipation solution for high-power-density components in these settings.

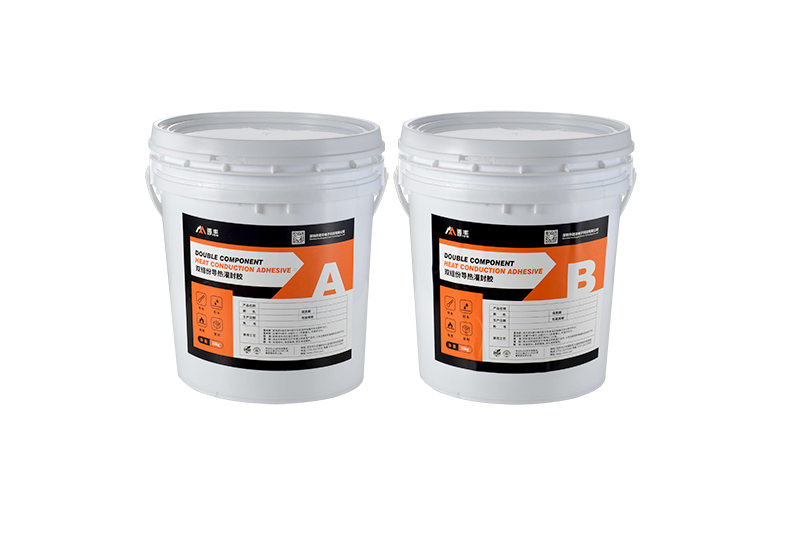
Characteristics:
● High Mechanical Strength and Electrical Insulation: Once cured, thermally conductive potting compound offers solid protection for electronic parts, preventing damage from physical forces and environmental factors like humidity, dust, and chemical corrosion.
● Superior Temperature Resistance: Thermally conductive potting compound maintains stable performance under high or extreme temperatures, widely used in industrial electrical equipment and in protecting components in high-temperature environments.
Application Scenarios:
Thermally conductive potting compound is widely used in applications with high requirements for sealing, protection, and heat dissipation, such as transformers, power modules, sensors, motors, and electronic control units. It is well-suited for components that require long-term, reliable encapsulation protection, especially in harsh working environments.

1.Material Characteristics Comparison
● Thermal Conductive Gel is a soft and elastic material that remains somewhat flexible after curing. It can accommodate deformation or thermal expansion of electronic components without applying excessive stress.
2.Primary Functional Differences
● Thermal Conductive Gel mainly functions to fill irregular surfaces or gaps, enhancing thermal conductivity. It focuses on providing high thermal performance without placing too much pressure on electronic parts, ideal for flexible heat dissipation applications.
3.Application Method Comparison
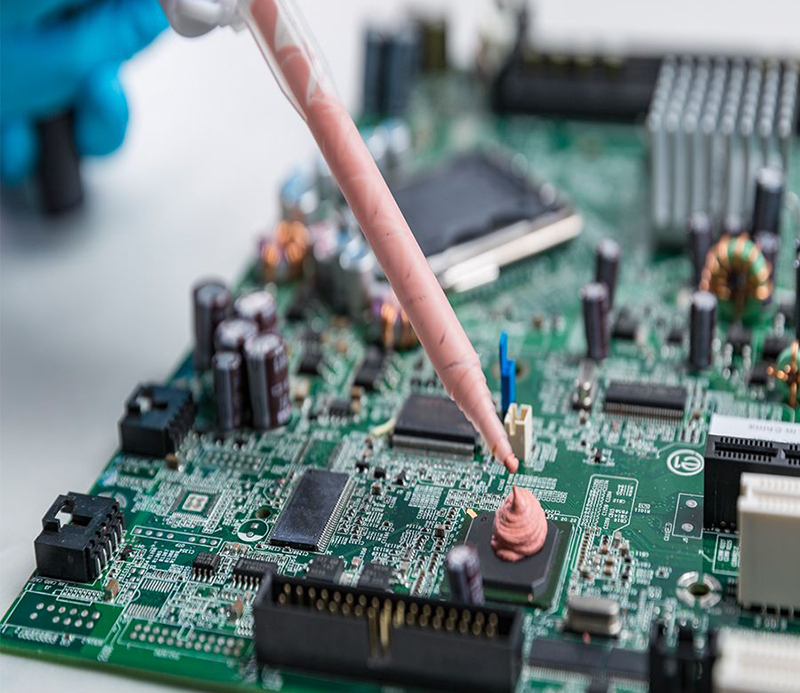
● Thermal Conductive Gel is typically applied by dispensing or scraping, with its flowability and adaptability allowing it to fill small gaps between electronic components, making it easy to handle and adaptable.
● Thermally Conductive Potting Compound is generally applied by pouring; once cured, it completely encases components, forming a solid protective shell. Potting is more complex, and the cured material is difficult to remove.
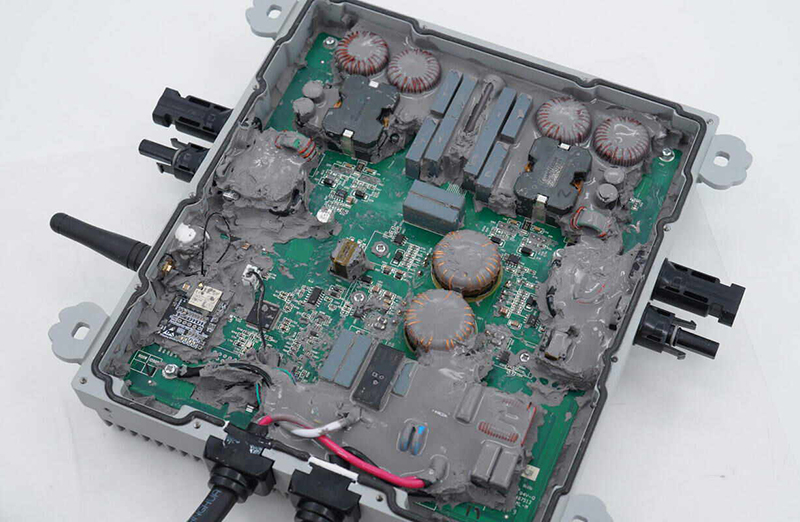
● Thermally Conductive Potting Compound is better suited for equipment requiring long-term sealing and protection, especially in harsh environments or with components that need high mechanical strength. For equipment that does not require frequent maintenance but requires long-term heat dissipation and protection, thermally conductive potting compound provides a stable, reliable solution.
 CN >
CN >