With the advancement of technology and the escalating consumer demands, household appliances, particularly personal care devices such as hair dryers, are evolving towards higher power, greater portability, and enhanced intelligence. However, increased power often exacerbates heat generation, posing a challenge to efficiently and safely manage heat dissipation – a pivotal aspect of industry innovation. Amidst this context, single-component thermal gel, as a novel thermal management material, is gradually emerging in hair dryer cooling solutions due to its unique performance advantages.
Status Quo and Challenges of Hair Dryer Cooling
Cooling Requirements for High-Power Hair Dryers
Modern, high-performance hair dryers boast increasingly powerful capabilities to meet user needs for rapid drying and styling. This heightened power operation, however, introduces severe cooling challenges. Inadequate or inefficient cooling not only impacts the longevity of the hair dryer but can also pose safety hazards like overheating-induced fires. Thus, effective cooling has become a crucial aspect of hair dryer design.
Limitations of Traditional Cooling Methods
Traditional cooling methods primarily include natural convection, forced air cooling, and liquid cooling. Natural convection relies on passive air movement and offers limited cooling efficiency; while forced air cooling enhances cooling capacity, it struggles with high-power devices. Liquid cooling, though highly effective, is hindered by complex systems and high costs, limiting its adoption in consumer electronics. Hence, identifying an efficient and cost-effective cooling solution is paramount.

Principles and Characteristics of Single-Component Thermal Gel
Basics of Thermal Conductive Materials
Thermal conductive materials function to rapidly transfer heat generated by electronic devices to the surrounding environment, preventing overheating. The performance of these materials is largely determined by their thermal conductivity coefficient, where a higher value denotes better cooling performance. Traditional materials such as metals and ceramics have limitations, including processing difficulties and weightiness.
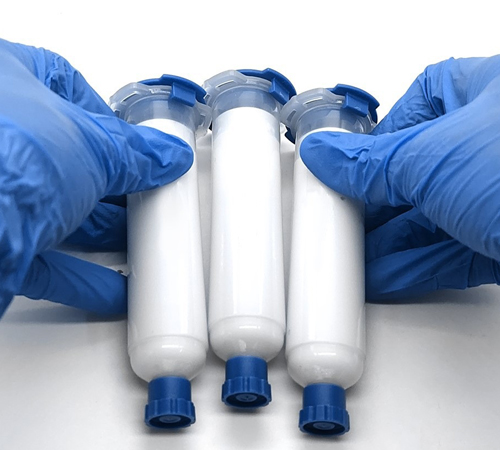
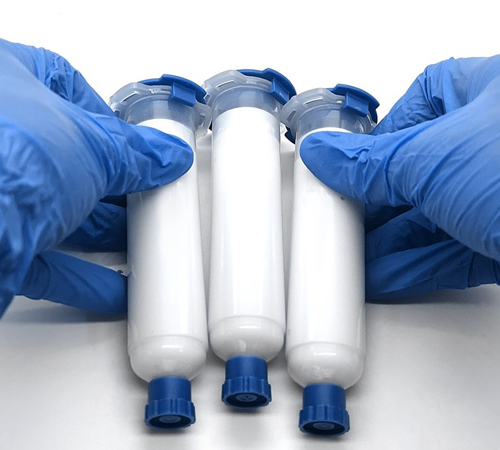
Composition and Characteristics of Single-Component Thermal Gel
Single-component thermal gel is a new type of thermal material composed mainly of thermally conductive fillers and a silicone matrix. The fillers, typically high-conductivity metal oxides like aluminum oxide and magnesium oxide, significantly enhance the gel's thermal properties. The silicone matrix imparts excellent flexibility and adhesion, enabling the gel to conform well to various complex surfaces and irregularities, thereby improving heat transfer efficiency.
Compared to traditional thermal materials, single-component thermal gels exhibit several distinct advantages:
- High thermal conductivity: The gel's thermal conductivity allows for rapid heat transfer.
- Excellent flexibility: The gel form adheres well to diverse surfaces, reducing thermal resistance effectively.
- Easy application: Single-component design eliminates the need for mixing and offers controllable curing time.
- High reliability: Thermal gels demonstrate good aging resistance, maintaining stable thermal performance over extended use.

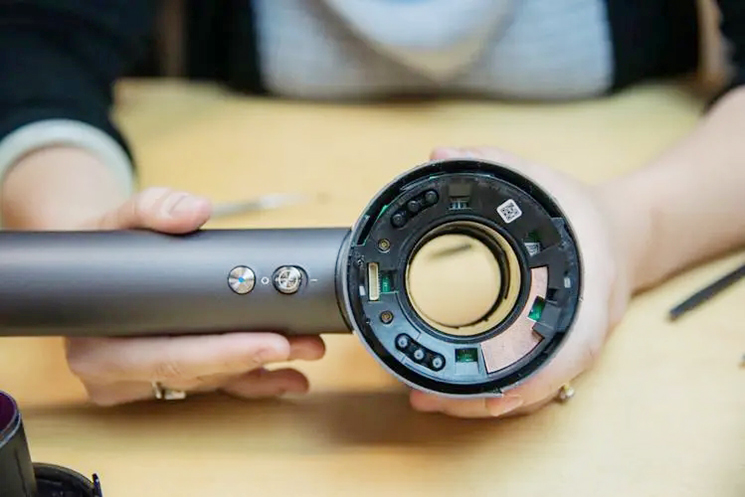
Application of Single-Component Thermal Gel in Hair Dryer Cooling
In hair dryer design, single-component thermal gel is primarily utilized in key areas:
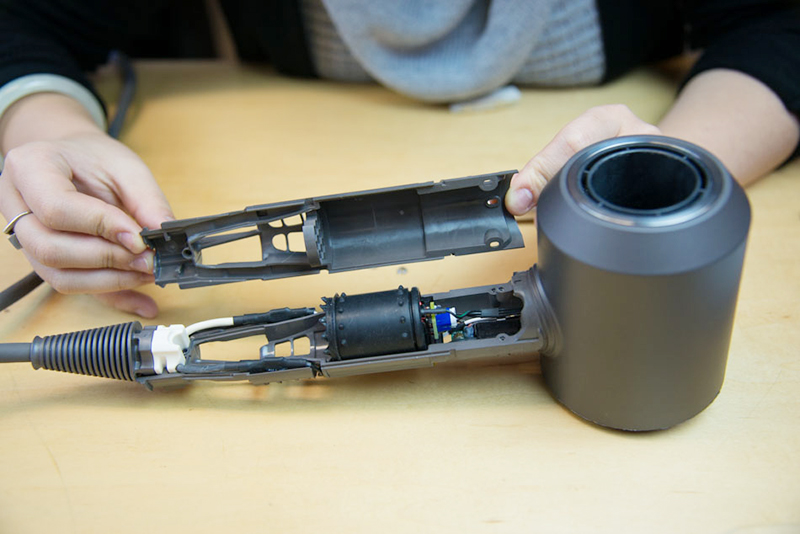
1. Heat Conduction between Motor and Housing: The motor, the primary heat source in a hair dryer under heavy load, generates substantial heat. Applying a thin layer of thermal gel between the motor housing and the external cooling shell significantly improves heat conduction efficiency, swiftly transferring heat for dissipation through natural convection or assisted fans.
2. Circuit Board Thermal Management: Modern hair dryers integrate numerous electronic components, with densely packed circuit boards contributing as significant heat sources. Using thermal gel between critical chips and heat sinks or the housing reduces component operating temperatures, prolongs lifespan, and boosts overall reliability.
3. Battery Module Cooling: For wireless hair dryers, the heat generated during battery charging and discharging is non-negligible. Strategic application of thermal gel between the battery pack and the housing effectively controls battery temperature, averting overheating risks.

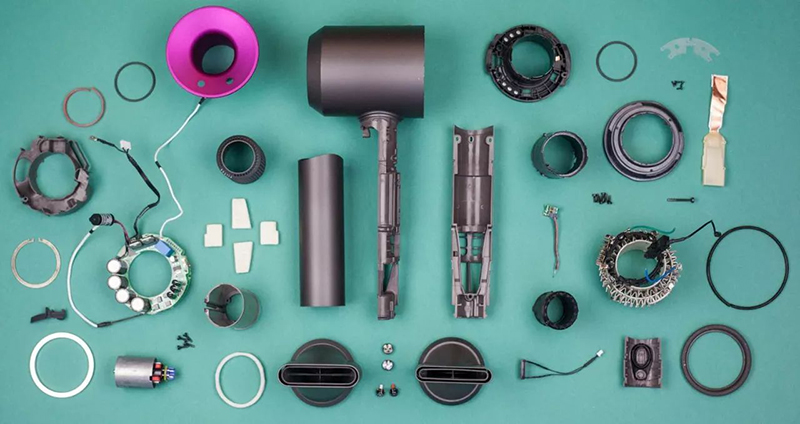
Implementation Challenges and Strategies
Despite the significant potential of single-component thermal gel in hair dryer cooling solutions, its application encounters challenges:
- Cost Consideration: Compared to conventional cooling materials, high-performance thermal gels are costlier, necessitating a balance between cost control and performance optimization.
- Material Selection and Ratio: Different applications require specific thermal conductivity, viscosity, etc., necessitating precise matching for optimal results.
- Production and Assembly Processes: Advancements in automated coating technology are crucial for mass adoption, requiring optimized processes to ensure uniform and contamination-free application.
To address these challenges, strategies include:
- R&D Collaboration: Strengthen collaboration with material suppliers to co-develop cost-effective products tailored to hair dryer requirements.
- Lean Production and Automation Upgrade: Introduce advanced automation for coating to enhance production efficiency and product consistency.
- Comprehensive Cost-Benefit Analysis: Considering lifecycle costs, weigh material expenses against performance improvements and reduced maintenance costs.
Conclusion
As consumer expectations for hair dryer performance and experience escalate, adopting single-component thermal gel as a cooling solution effectively tackles the challenges posed by high power, facilitating miniaturization, lightweight designs, and smarter products. By tackling implementation challenges through technological innovations and process optimizations, its application scope can be widened, driving the technological advancement and market competitiveness of the personal care appliance industry. With ongoing advancements in material science and declining costs, the use of single-component thermal gels in hair dryers and other electronic device cooling will broaden, ensuring safer, more efficient, and comfortable user experiences.




 CN >
CN >