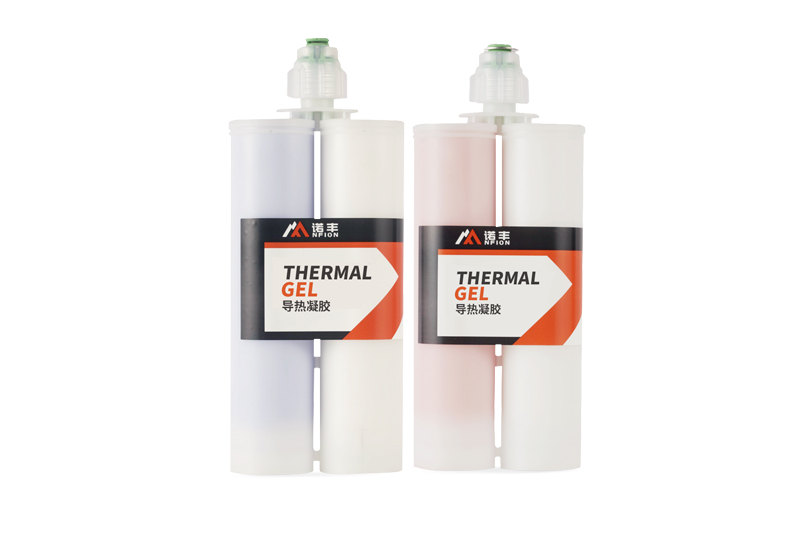
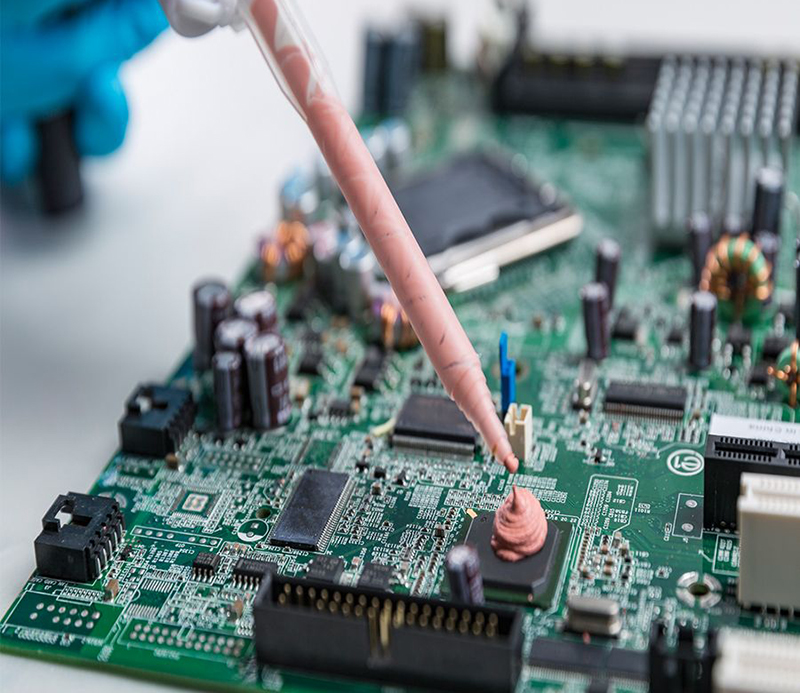
Double-Component Thermal Gel Industry Standard
Author:NFION
Date:2025-06-05 10:01:31
In the current trend of electronic devices becoming smaller and more high-performance, thermal management has emerged as a critical factor limiting their stable operation and lifespan. Traditional thermal interface materials often struggle to meet stringent heat dissipation demands. However, double-component thermal gels, with their excellent thermal conductivity, superior reliability, and flexible application characteristics, are increasingly becoming the new favorite in the field of thermal management. As their application scope continuously expands, establishing a comprehensive set of industry standards to ensure product quality, stable performance, and application safety has become an urgent necessity.

Why Do Double-Component Thermal Gels Need Industry Standards?
Double-component thermal gels typically consist of Part A (base material) and Part B (curing agent), forming an elastic thermal conductive material upon mixing and curing. Their performance is influenced by various factors, including raw material purity, formulation ratio, mixing process, curing conditions, and storage environment. A lack of unified industry standards could lead to:
● Inconsistent Product Quality: Significant performance differences between thermal gels from different manufacturers, and even batch-to-batch variations from the same manufacturer, introduce uncertainty for downstream applications.
● Misleading Performance Specifications: Some products might exaggerate key metrics like thermal conductivity and temperature resistance range, misleading users' choices.
● Increased Application Risks: Inferior products may experience cracking, delamination, or thermal performance degradation during long-term use, potentially even leading to equipment failure.
● Disorderly Industry Competition: The absence of standards will lead to vicious price competition, hindering technological innovation and healthy industry development.
Therefore, establishing a scientific and comprehensive set of industry standards is crucial for safeguarding consumer rights and promoting healthy industry development.

Key Aspects of the Standard: A Full-Lifecycle Consideration from Material to Application
The industry standard for double-component thermal gels should cover every aspect from raw materials to final application, ensuring product quality and performance throughout its entire lifecycle.
1. Raw Material Standards and Control
Raw materials are the foundation determining the performance of thermal gels. The standard should specify:
● Thermal Fillers: Define key indicators such as purity, particle size distribution, morphology, and specific surface area for common thermal fillers (e.g., aluminum oxide, boron nitride, silicon nitride, silicon carbide). For novel thermal fillers, corresponding performance evaluation methods should be included.
● Polymer Substrates: Clarify key parameters for polymer substrates like silicone and epoxy resins, including molecular weight, viscosity, and functional group content, to ensure their thermal stability, chemical stability, and compatibility with fillers.
● Curing Agents and Additives: Specify the activity and purity of curing agents, and the type, content, and safety requirements for additives such as antioxidants, coupling agents, and rheological aids.
2. Product Performance Indicators and Test Methods
This is the core of the standard, directly related to the effectiveness of thermal gel applications. The standard should define and unify test methods for the following performance indicators:
● Thermal Conductivity: Utilize internationally recognized steady-state methods (e.g., hot wire method, laser flash method) or transient methods, specifying test temperatures, pressures, and other conditions to ensure accuracy and comparability of results.
● Thermal Resistance: Define test methods and standards for specific application scenarios to evaluate the material's heat dissipation efficiency at the actual interface.
● Viscosity: Specify the viscosity range for Part A and Part B, as well as the operational viscosity after mixing, to ensure ease of dispensing and coating.
● Pot Life & Curing Time: Clearly define the usable time (from mixing until a significant increase in viscosity) and the time required for complete curing at specific temperatures.
Hardness: Measure the hardness of the cured material using a Shore durometer to reflect its mechanical properties and reliability.
● Dielectric Properties: For electronic and electrical applications, dielectric strength, dielectric constant, and dielectric loss should be tested to ensure electrical insulation performance.
● Thermal Stability & Reliability: Conduct reliability tests such as high-temperature aging, high-humidity aging, and thermal shock to evaluate the material's performance stability under extreme conditions.
● Volatile Organic Compound (VOC) Content: Limit the release of harmful substances to comply with environmental and health requirements.
3. Production Process and Quality Control
The standard should guide manufacturers in establishing a rigorous quality management system, including:
● Mixing Equipment and Process: Specify the type of mixing equipment, mixing speed, time, and other parameters to ensure uniform mixing of Part A and Part B, preventing air bubble formation.
● Degassing Treatment: Require vacuum degassing of the mixed gel to eliminate internal air bubbles, improving thermal efficiency and reliability.
● Packaging and Storage: Clearly define product packaging materials, sealing requirements, and optimal storage temperature, humidity, and shelf life to prevent product failure.
● Batch Management and Traceability: Establish a complete batch number management system to ensure full traceability of products from raw materials to finished goods.
4. Application Guidelines and Safety Standards
In addition to the product itself, the standard should provide clear application guidelines to prevent improper operation and potential risks:
● Surface Cleaning and Treatment: Specify cleaning requirements for the substrate surface before dispensing, such as degreasing and dust removal, to ensure good adhesion and a thermal interface.
● Dispensing and Coating Methods: Provide recommended parameters and precautions for different application methods, such as manual dispensing and automated equipment dispensing.
● Curing Conditions: Emphasize strict control of curing temperature and time to achieve optimal performance.
● Safe Operating Procedures: Remind operators to wear protective equipment, avoid direct contact, and provide emergency handling measures.
● Waste Disposal: Guide users on environmentally friendly disposal of waste thermal gel and packaging materials.
Looking Ahead: Standardization Leading Industry Upgrades
The establishment of an industry standard for double-component thermal gels will not only be about defining a series of technical parameters, but also an opportunity for overall industry upgrade. It will:
● Improve Product Quality: Encourage companies to focus more on product R&D and quality control, eliminate inferior products, and elevate the overall industry standard.
● Promote Technological Innovation: Clear standards will incentivize companies to invest more resources in technological innovation beyond basic requirements, developing more excellent and widely applicable new thermal gels.
● Regulate Market Order: Reduce false advertising and vicious competition, providing a fair competitive environment for high-quality products.
● Safeguard User Rights: Ensure users can choose stable, safe, and reliable products, reducing application risks.
● Promote International Cooperation: Aligning with international standards will help Chinese double-component thermal gel products enter the global market and participate in international competition.
The future of double-component thermal gels holds immense possibilities. As electronic products evolve towards higher power, smaller size, and more complex functions, the demand for thermal management will become even more pressing. A sound industry standard is the ballast that will enable this ship to brave the waves and sail into a new era. Let's work together to drive the double-component thermal gel industry towards a more standardized, efficient, and sustainable future.
 CN >
CN >