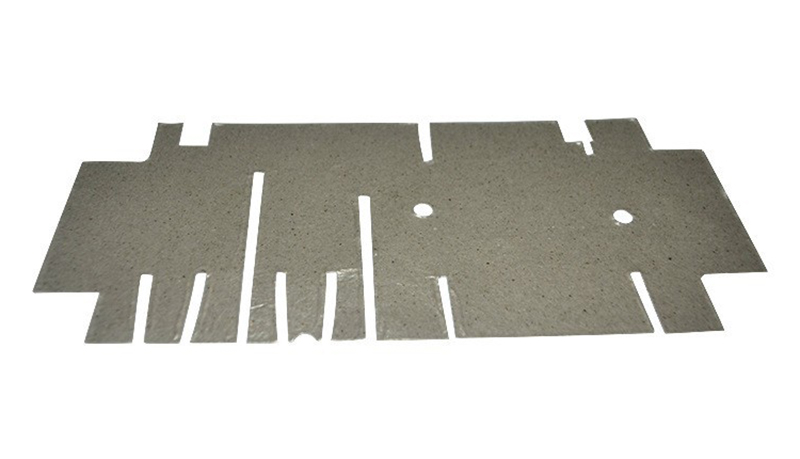
Overview of Mica Sheet Material Characteristics
Mica sheets are thin sheets processed from natural mica minerals, which are silicate minerals primarily composed of silicon, oxygen, aluminum, magnesium, and iron. Mica has a crystalline structure that allows it to separate into thin layers. This unique molecular structure gives mica sheets excellent insulation properties, high-temperature resistance, and superior tensile and flexural strength.
Mica can be classified into two main types based on its chemical composition and structure: muscovite and phlogopite. Muscovite is commonly used in electronic and electrical equipment, while phlogopite is widely applied in high-temperature fields due to its higher thermal resistance. The material characteristics of mica sheets make them valuable across various industries.

Main Functions and Applications of Mica Sheets
The properties of mica sheets make them suitable for a wide range of industrial applications. Their main functions are as follows:
1. Electrical Insulation
Mica sheets possess excellent electrical insulation properties, maintaining electrical stability even in high-temperature or high-humidity environments. This makes them an ideal insulating material for high-voltage electrical equipment, transformers, motors, and generators. Mica sheets not only prevent current leakage but also extend equipment lifespan and enhance safety.
2. High-Temperature Protection
Mica sheets exhibit exceptional heat resistance. Phlogopite can withstand temperatures above 1000℃, while muscovite can tolerate up to about 500℃. This feature makes mica sheets widely used in high-temperature equipment and facilities, such as insulation for heating elements and arc protection components. In high-temperature industries like steel and metallurgy, mica sheets are also employed to protect critical equipment and electronic components from heat.
3. Corrosion Resistance
Mica sheets are chemically stable and highly resistant to acids and alkalis, making them an effective anti-corrosion material in chemical production. They help protect other materials or equipment from chemical corrosion, extending the equipment's lifespan and improving overall operational safety.
4. Heat Dissipation and Thermal Management in Electronics
Besides insulation, mica sheets also assist in heat management for electronic components. Due to their layered structure, they can conduct a certain amount of heat while maintaining insulation, making them suitable as thermal management materials in precision electronics. In devices operating in high-temperature environments, mica sheets can effectively dissipate heat and prevent overheating of electronic components.
5. Building and Decorative Materials
Mica sheets are also used in construction, especially for fireproof and waterproof building materials. Their excellent fire-resistant properties and aesthetic appearance make them ideal for fireproof wall coatings, insulating layers, and wall decorative panels, enabling protective functionality alongside an appealing appearance.

Advantages and Disadvantages of Mica Sheets
1. Advantages
● Excellent Insulation: Mica sheets maintain insulating properties in high temperatures and humid environments, making them ideal for electrical insulation.
● High Heat Resistance: They are the preferred material for thermal protection due to their stability at high temperatures.
● Corrosion Resistance: Mica sheets can endure acid and alkali environments for extended use without significant chemical changes.
● High Physical Strength: They exhibit good stability under tensile and bending stress.
2. Disadvantages
● Difficult to Process: Natural mica sheets are typically brittle and can break easily during processing, requiring specialized techniques.
● Relatively Expensive: High-quality mica sheets are costly, which increases application costs.
● Size Limitations: Due to the size limitations of natural mica, mica sheets may have restrictions in size and thickness, limiting their use in large-scale applications.
Future Prospects of Mica Sheets
With technological advancements, the manufacturing techniques and application scenarios for mica sheets are expanding. In the future, mica sheets may find broader applications in high-tech fields. For instance, in 5G equipment and advanced electric vehicle (EV) batteries, mica sheets offer more efficient thermal management solutions. Moreover, as demand for eco-friendly materials rises, the natural and renewable characteristics of mica sheets may secure them a vital role in the materials market of the future.
Conclusion
Mica sheets, with their excellent electrical insulation, high-temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance, have become essential materials in electrical equipment, electronic devices, chemical anti-corrosion, and building decoration. Although mica sheets face some limitations in processing and application, their unique properties make them irreplaceable in many industries. In the future, with the progress of materials science and manufacturing techniques, the applications of mica sheets will become more diverse, supporting high-tech industries and green development.



 CN >
CN >