Two-component thermal gels are widely used in thermal management for electronic products due to their excellent thermal conductivity and flexible application. However, in practice, curing too quickly is a common issue, especially in complex production environments with multiple operational steps. If not properly handled, this phenomenon can lead to material waste, process instability, and even performance degradation of the product. So, what are the causes of fast curing in two-component thermal gels? What measures can be taken to address this issue?

1. Causes of Fast Curing in Thermal Gels
1.1 Issues with Formula Design
The curing process of two-component thermal gels is determined by their chemical composition, typically through the curing reaction of components A and B. If the curing speed is too fast, it may be due to a high concentration of curing agents or an overly active curing reaction in the formula design. For example, an excessive proportion of catalysts can accelerate the reaction, causing the material to cure before the application is complete.
1.2 Environmental Factors
Environmental temperature and humidity significantly affect the curing speed of thermal gels. In high-temperature conditions, chemical reactions will accelerate, shortening the curing time. Additionally, high humidity can affect the curing process of certain two-component thermal gels, especially those sensitive to moisture. Fluctuations in these environmental conditions may prevent operators from accurately controlling the curing speed.
1.3 Uneven Mixing
Two-component thermal gels need to be mixed accurately before use. If the mixture is uneven, some areas will have a higher concentration of reactants, accelerating the curing process and leading to uneven or excessively fast local curing.
1.4 Inadequate Control of Working Time
The pot life (working time) of mixed two-component thermal gels is usually limited. If operators fail to complete the application within this window, the gel will begin to cure gradually, making it unusable. Therefore, improper time management or slow operational procedures during the process may result in curing that is too fast.

2. How to Address the Problem of Fast Curing in Two-Component Thermal Gels
2.1 Optimizing Formula Design
Adjusting the formula of thermal gels based on actual application needs is a key method for extending curing time. Reducing the proportion of curing agents or catalysts can slow down the chemical reaction. Additionally, for environments with high temperature or humidity, selecting materials more resistant to environmental changes ensures a stable curing speed under different conditions.
2.2 Controlling the Working Environment
Improving the working environment is an effective way to extend the curing time of two-component thermal gels. In high-temperature environments, lowering the temperature can slow down the chemical reaction. For instance, using air conditioning systems or localized cooling equipment can control the workspace temperature. Additionally, using dehumidifiers to reduce air humidity can prevent accelerated curing caused by high humidity.
2.3 Using Automated Mixing Equipment
To ensure that the two components of the thermal gel are mixed evenly, it is recommended to use automated mixing equipment. These machines can accurately mix components A and B according to preset ratios, avoiding the issue of uneven mixing caused by human factors. Automated equipment also improves efficiency, shortens operational time, and reduces curing problems caused by overly long handling times.
2.4 Properly Planning Application Time
During the application process, operational steps should be planned to ensure that mixing and application are completed within the gel’s pot life. Before use, it’s essential to understand the pot life and curing time of the selected thermal gel and adjust production processes accordingly to ensure smooth application. Additionally, for projects that require longer application times, choosing products with a longer curing time may be more appropriate.
2.5 Choosing Slow-Curing Formulas
There are slow-curing two-component thermal gel formulas on the market specifically designed for applications that require extended handling time. These materials are designed to extend the curing time while ensuring that the final physical and chemical properties remain intact. In large-scale production involving two-component thermal gels, using slow-curing formulas can be an effective strategy.
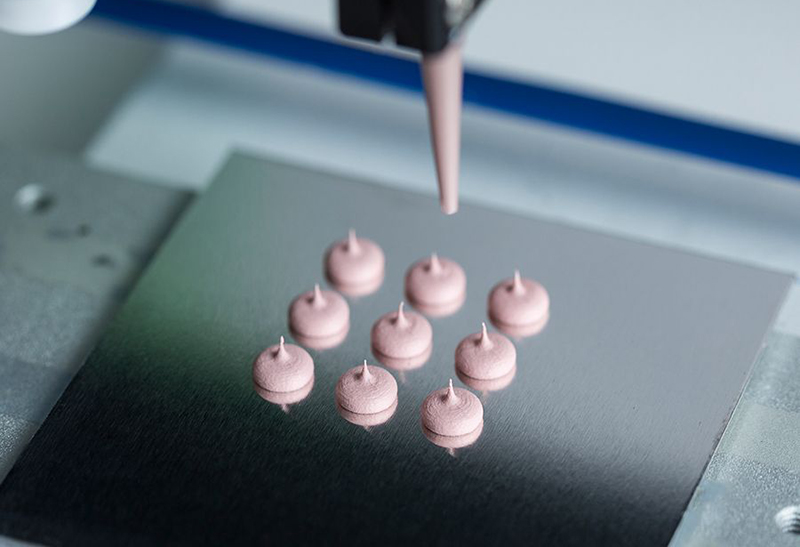
3. Conclusion
Curing too fast is a common problem with two-component thermal gels, but by making appropriate adjustments to the formula, environment, equipment, and workflow, the curing process can be effectively delayed, ensuring the smooth application of the material. When addressing fast-curing issues, it is essential to accurately analyze the cause and then take targeted actions, such as optimizing the formula, controlling the environment, or using automated equipment. These measures can improve production efficiency, reduce material waste, and ensure the stability of product performance.
Choosing the right thermal gel formula and application process for different use cases will help enhance overall product performance and lifespan.



 CN >
CN >