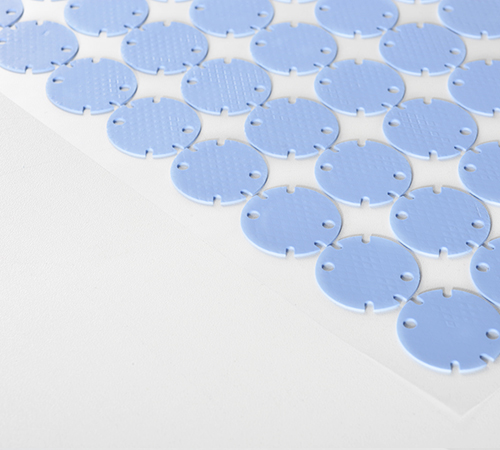
In electronic devices and thermal management systems, thermal conductive silicone pads play a pivotal role. Their exceptional heat conductivity, sound insulation properties, and compressibility make them an ideal choice for heat transfer and cooling. However, over time and with changes in operating environments, thermal conductive silicone pads may exhibit failure phenomena. This article delves into the meaning, causes, impacts, and countermeasures of thermal conductive silicone pad failures.
- Aging and Degradation: Over time, the polymer chains in the silicone pads may undergo breakdown or cross-linking due to exposure to heat, oxygen, light, or other environmental factors, leading to a decline in material properties.
- Stress Relaxation: Under high temperatures and sustained pressure, stress relaxation can occur in the silicone pads, reducing their adhesive strength to contact surfaces and affecting heat transfer efficiency.
- Contaminants and Impurities: Environmental contaminants and impurities can infiltrate the silicone pads, chemically reacting or physically interacting with them, damaging their structure and functionality.
- Design or Manufacturing Defects: Flaws in the design or manufacturing process of the silicone pads, such as incorrect material ratios or lax production controls, can lead to material instability or predisposition to failure.
- Reduced Thermal Conductivity Efficiency: Following failure, the decreased thermal conductivity hampers effective heat transfer, impacting the device's cooling performance.
- Decline in Device Performance: Reduced thermal conductivity leads to increased device temperatures, affecting performance and stability. Prolonged high-temperature operation can expedite device aging and shorten its lifespan.
- Optimize Material Formulation: Enhance the silicone pad's resistance to aging, degradation, and chemical stability by improving its material composition, thereby prolonging its service life.
- Strengthen Quality Control: Enhance quality control and inspection during manufacturing to ensure products meet design standards. Promptly address or replace defective products.
- Regular Maintenance and Inspection: Schedule maintenance and inspections of in-use silicone pads to promptly identify and address potential failure issues, including cleaning, securing, or replacing them as needed.
- Improve Design and Manufacturing Processes: Revise the design and manufacturing processes of silicone pads to minimize potential failure points, through structural optimization, process improvement, and efficiency enhancement.
 CN >
CN >