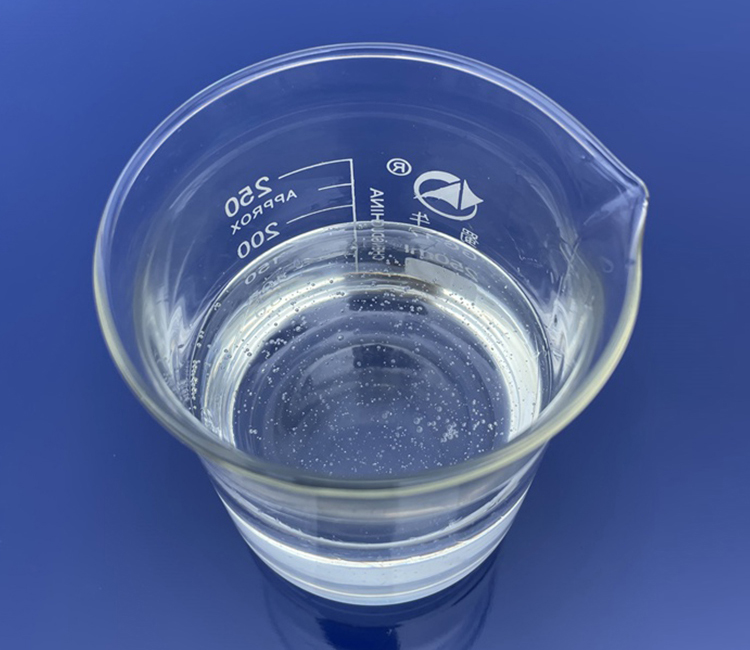
Thermal oil, also known as heat transfer oil or heat medium oil, is a specialized heat transfer medium utilized in industrial and commercial applications. Its primary function revolves around conducting heat to warm or cool systems or equipment, thereby achieving stable and efficient temperature control. Thermal oils are extensively employed across industries such as chemicals, petroleum, plastics, rubber, textiles, dyeing, food processing, and wood processing, among others. This article comprehensively delves into the realm of thermal oil, covering aspects including its definition, types, characteristics, applications, and advantages.
Mineral Oil-Based Thermal Oil
Synthetic Thermal Oil
Silicone-Based Thermal Oil
Thermal Stability: Essential for maintaining integrity without decomposition or deposit formation under high temperatures.
High Boiling Point and Low Freezing Point: Ensuring no evaporation at high temperatures and preventing crystallization or thickening at low temperatures for maintained fluidity.
High Thermal Conductivity Efficiency: A core requirement for effective heat transfer to targeted systems or equipment.
Low Viscosity Variation: Maintaining low viscosity changes over a wide temperature range for continuous and stable heat transfer in the system.
Oxidation and Aging Resistance: Prolonging lifespan, reducing replacement frequency, and minimizing maintenance costs by resisting degradation at high temperatures.
Chemical Industry: Providing stable and accurate temperature control essential for safe and efficient reactions in controlled high-temperature environments.
Petroleum Processing: Critical in processes like distillation and cracking, used for crude oil heating and separation into various products.
Plastics and Rubber Industries: Heating molds and extrusion equipment to ensure even heating and optimal processing temperatures for product quality and productivity.
Textile and Dyeing: Heating dye vats and drying equipment for uniform dye distribution and adherence to fibers, vital for high-quality dyeing results.
Food Processing: Used in boilers and baking equipment, ensuring uniform heat distribution and enhancing product quality and safety.
Advantages of Thermal Oil
Efficient Heat Conduction: Rapid heat transfer reduces energy consumption and enhances production efficiency.
Lower Operating Pressure: Systems typically operate at lower pressures, reducing safety risks associated with high-pressure equipment and simplifying system design.
Broad Operating Temperature Range: Functionality across a wide temperature spectrum, maintaining stable physical and chemical properties to meet diverse industrial needs.
Long Service Life: High-quality thermal oils with strong oxidation and aging resistance last longer, reducing replacement and waste disposal costs and environmental impact.
Flexible System Design: Adaptable to different process requirements and equipment layouts, enabling precise temperature control for complex manufacturing processes.
System Cleaning: Thorough cleaning before initial use prevents impurities from affecting oil performance.
Temperature Control: Strict adherence to operational temperature ranges avoids overheating and oil degradation.
Regular Monitoring: Checking physical and chemical parameters of the oil, such as viscosity, acid value, and flash point, for timely oil replacement.
Leak Prevention: Periodic inspection of seals prevents oil leaks, avoiding environmental pollution or fire hazards.
Antioxidant Management: Using antioxidants or deoxygenation devices to retard oil aging.
Environmental Upgrades: Developing more bio-based, biodegradable thermal oils to reduce environmental impact.
Energy Efficiency Improvement: Researching novel thermal oil materials with higher heat transfer efficiency and lower energy consumption.
Smart Management: Leveraging IoT technology for remote monitoring and intelligent maintenance of thermal oil systems.
Thermal oil, as an efficient and reliable heat transfer medium, plays an indispensable role in modern industrial production. By selecting appropriate thermal oil types and implementing correct usage and maintenance practices, significant enhancements in production efficiency, energy savings, and operational costs can be achieved. As technology progresses and new materials are developed, the performance and application scope of thermal oils will expand further, providing premium heat transfer solutions across industries.
Thermal oil not only bolsters industrial productivity but also champions environmental protection and safety. With rising environmental standards, its application will expand, contributing to sustainable development. When choosing and using thermal oil, enterprises should holistically consider its properties, application requirements, and economic benefits to ensure the thermal system operates efficiently, safely, and with long-term stability.
 CN >
CN >