As AI models grow more complex, the demand for computing power is skyrocketing. High-performance AI servers have become the backbone for large-scale model training and inference. However, rising power consumption brings an unavoidable issue: excessive heat. So, what exactly happens when an AI high-computing server overheats? Is it merely a matter of slowing down? This article dives into the technical risks, performance bottlenecks, and long-term consequences of overheating in AI servers.
Why Do Servers Overheat?
In AI servers, core components like CPUs, GPUs, and TPUs often run at full load for long periods. Their power consumption can reach several hundred to over a thousand watts. All that power ultimately turns into heat. If the cooling system is insufficient, heat accumulates, and the temperature rises. Common causes include:
● Long AI training times and sustained workload
● High power density due to multi-card configurations
● Poor thermal design: blocked airflow, inefficient heat paths
● High ambient temperature or HVAC failure
Five Major Risks of Overheating
1. Performance Throttling
Modern processors have built-in thermal throttling. When core temperatures exceed thresholds (e.g., 85°C), the system automatically reduces frequency to prevent damage. This thermal throttling significantly slows down computing, especially in latency-sensitive inference tasks.
2. Shortened Hardware Lifespan
Heat accelerates aging. Transistors, capacitors, and inductors in GPUs degrade faster under prolonged high-temperature conditions. This leads to early failure due to micro-damages like solder fatigue or package delamination.
3. System Instability
Excess heat can cause crashes, reboots, and blue screens. Worst-case, it may interrupt ongoing tasks or corrupt data—a major loss for long AI training cycles.
4. Higher Energy and Operational Costs
Overheating causes fans to spin faster and cooling systems to work harder, increasing overall energy consumption. More maintenance is also required, adding to operational overhead.
5. Increased Safety Risks
In extreme cases, local overheating can burn out power modules or cause thermal runaway and fire hazards—especially in older systems with poor heat dissipation design.
Why AI Servers Are Prone to Overheating
Compared to traditional servers, AI servers exhibit these "hot" characteristics:
● High-Density Deployment: A single server may house multiple GPUs or TPUs like NVIDIA A100 or H100, each consuming over 300W, pushing the total thermal design power (TDP) to 1kW+.
● Sustained Heavy Load: Model training often lasts days or weeks, placing continuous stress on cooling systems.
● Complex Cooling Requirements: Multiple modules and dense interconnections demand more than just basic air cooling or low-grade thermal materials.
How to Address Overheating: Thermal Management Solutions
Comprehensive strategies are required to tackle the thermal challenges in AI servers:
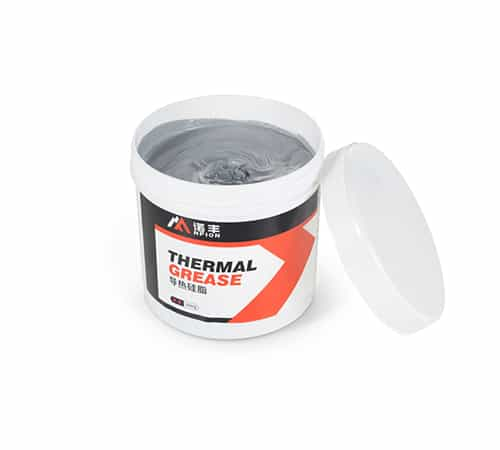
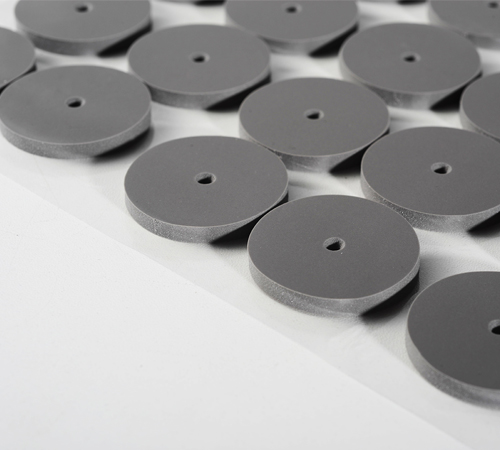
1. High-Performance Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs)
Thermal grease, thermal gels, and thermal pads significantly reduce thermal resistance between chips and heat sinks. For multi-GPU systems, high thermal conductivity TIMs (e.g., >6W/m·K gels) can lower junction temperatures and prevent thermal bottlenecks.
2. Advanced Cooling Methods: Liquid and Immersion Cooling
Air cooling often falls short for AI server heat loads. Liquid cooling (cold plates or immersion systems) is increasingly mainstream, offering high thermal efficiency and precise temperature control.
3. Optimized Structural Design
Improved airflow, heat exchangers, and layered thermal layouts can enhance dissipation. Proper rack airflow management avoids hot spots and ensures smooth air movement.
4. Intelligent Thermal Control Systems
Temperature sensors paired with smart algorithms can dynamically manage fan speeds, workload distribution, and task scheduling for real-time thermal control.
Conclusion: High Performance Requires Cool Thinking
AI is transforming industries, and high-performance servers are its backbone. But performance gains must not come at the cost of thermal imbalance. Overheating can compromise stability, efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and safety.
Organizations must take a proactive approach to thermal management—across materials, design, and systems—to build robust AI infrastructures.
Heat isn’t a minor issue; it defines the boundary between peak performance and potential failure.
For professional guidance on selecting and applying thermal materials for AI servers, feel free to contact our technical team.

 CN >
CN >