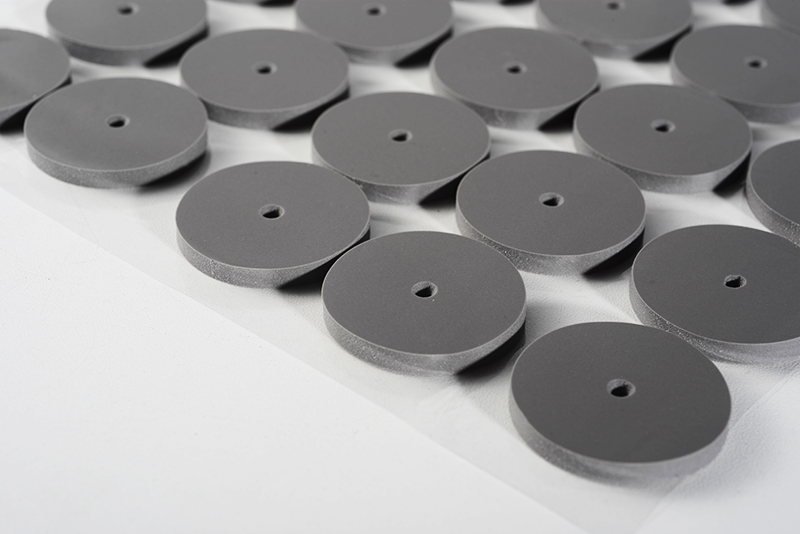
Selecting the correct thermal pad size is crucial in ensuring optimal thermal conductivity and efficient heat dissipation for electronic devices. Whether you are working on a CPU, GPU, or power electronics, the right fit of a thermal pad can make a significant difference in the performance and longevity of the device. NFION Thermal will guide you through the process of determining the proper thermal pad size for your application, covering key factors such as measuring, material properties, and common industry practices.
Understanding Thermal Pads and Their Importance
Thermal pads are essential components used in thermal management to enhance the heat dissipation between heat-generating components (e.g., processors, transistors) and heat sinks or other cooling solutions. They are typically made from materials with high thermal conductivity and are designed to fill the microscopic gaps between surfaces, ensuring efficient heat transfer.
Choosing the right thermal pad size is vital because an improperly sized pad can lead to poor heat transfer, overheating, or even component failure.
Step-by-Step Guide to Determining the Correct Thermal Pad Size
Step 1: Measure the Heat-Generating Surface
To ensure the thermal pad fits properly, you need to accurately measure the dimensions of the heat-generating component or surface. For instance:
● Width and Length: Use a ruler or caliper to measure the exact length and width of the chip or component that needs cooling.
● Height or Thickness: Some components may have an uneven surface, so measure the height or thickness if it is relevant to the pad's fit.
It's essential to take precise measurements to ensure the thermal pad will cover the entire surface of the component and make proper contact with the heat sink or cooling system.
Step 2: Determine the Thickness of the Thermal Pad
The thickness of the thermal pad is another critical factor. A pad that is too thin may not fill the gap properly, while a pad that is too thick can create excess pressure on the component, potentially leading to damage.
● Ideal Thickness: Most thermal pads are available in thicknesses ranging from 0.3 mm to several millimeters. Choose a thickness that matches the gap between your component and the cooling system. You may need to consult technical specifications or guidelines from the manufacturer for the recommended thickness for your particular device.
● Compressibility: Some thermal pads are designed to compress when pressure is applied, filling any remaining gaps. This can be beneficial in situations where the exact gap measurement is difficult to determine.
Step 3: Account for Pad Alignment and Overlap
Ensure that the thermal pad completely covers the area that needs cooling. It should be slightly larger than the surface area of the component to allow for slight misalignments or shifts during installation. However, avoid selecting a pad that is too large, as excess material may cause problems, such as short circuits or uneven pressure distribution.
● Pad Size: The pad should cover the entire heat-generating surface but should not hang over the edges, as this can interfere with other components or cause overheating.
Step 4: Consider the Material Properties
Different thermal pad materials have different thermal conductivities, compressibilities, and thermal resistance characteristics. Understanding these properties can influence your decision on the ideal thermal pad size and type for your application.
● Thermal Conductivity: Higher thermal conductivity pads are more efficient at transferring heat and are often used in high-performance applications like gaming computers or data centers.
● Compression and Conformability: Some materials conform better to irregular surfaces, which may reduce the need for precise measurements in certain situations.

Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Choosing a Thermal Pad Size
● Choosing a Pad That is Too Small: A thermal pad that is too small will not make sufficient contact with the component or the cooling solution, leading to inefficient heat dissipation.
● Overcompensating with a Larger Pad: While a slightly larger pad can be beneficial, a pad that is too large can create mechanical issues or interfere with adjacent components.
● Neglecting Surface Preparation: Ensure that both the surface of the component and the heat sink are clean before applying the thermal pad. Dirt, dust, or residues can significantly reduce the pad's effectiveness.
Industry Best Practices for Selecting Thermal Pads
● Consult Manufacturer Specifications: Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines for your specific device or component to determine the recommended thermal pad thickness and material.
● Test and Measure: In some applications, it’s beneficial to test different pad sizes to achieve the best thermal performance.
● Use Pads with High-Quality Materials: High-performance materials, such as silicone-based thermal pads, are often preferred for their superior heat conductivity and reliability.
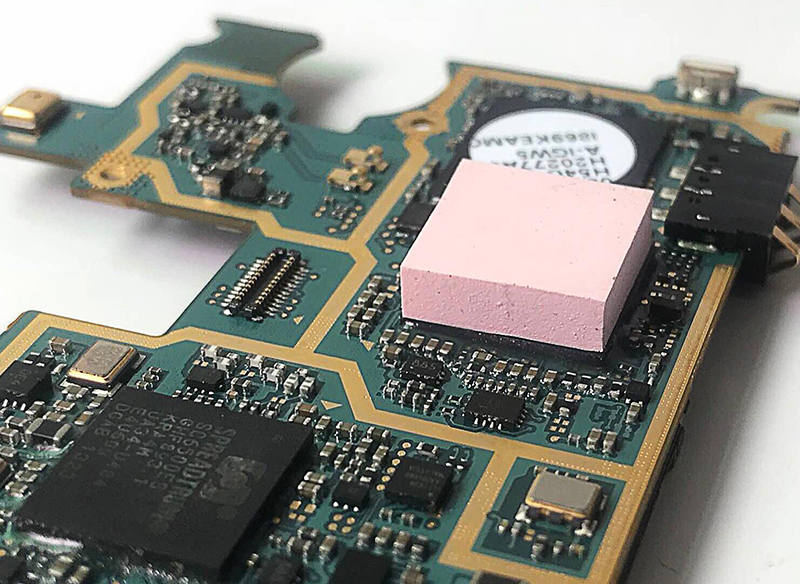
Conclusion
The correct thermal pad size is essential for effective thermal management in electronic systems. By carefully measuring the component surfaces, selecting the appropriate thickness, and considering material properties, you can ensure that your thermal pad provides optimal performance. Understanding these considerations and avoiding common pitfalls will help you achieve efficient heat dissipation and prolong the lifespan of your devices.
For those who are unsure or working with complex systems, consulting with experts or utilizing custom solutions may be the best way to guarantee the ideal fit for your thermal pad.



 CN >
CN >