Efficient heat management is paramount in the performance and longevity of electronic and electrical devices. Two prominent thermal interface materials (TIMs) used for heat dissipation are thermal pads and thermal grease. Each has distinct characteristics that cater to different applications. This article delves into the properties, applications, advantages, and disadvantages of thermal pads and thermal grease to provide a thorough understanding and help readers make informed decisions.
Understanding Thermal Pads
Composition and Structure
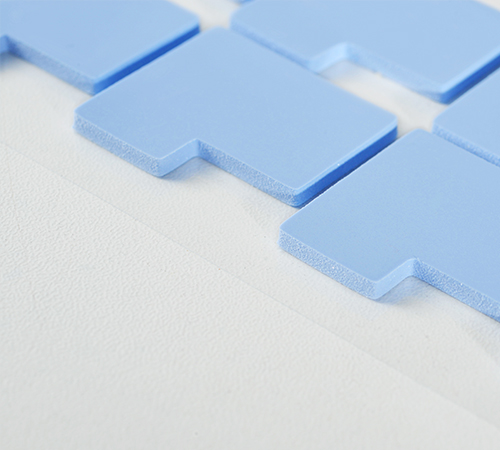
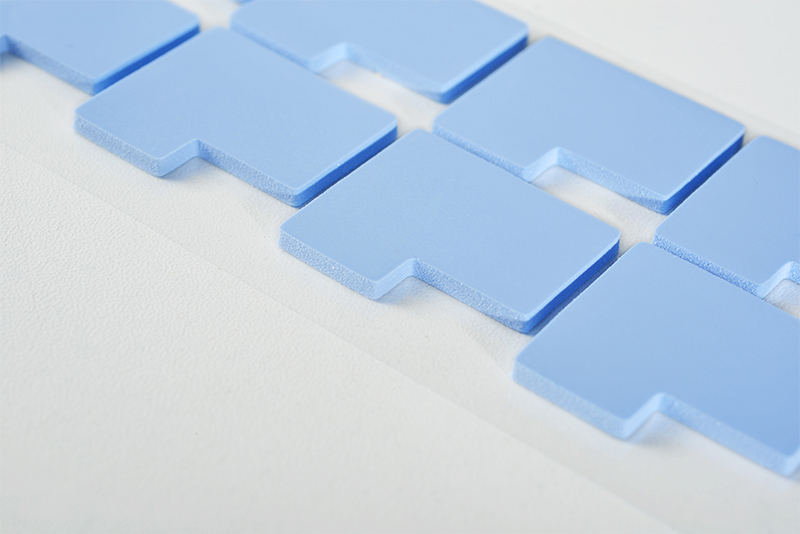
Thermal pads, often made from silicone rubber embedded with thermally conductive fillers like ceramic or metallic particles, are flexible, conformable sheets. These pads come in various thicknesses, typically ranging from 0.3 mm to several millimeters, and can be customized for specific requirements.
Key Characteristics
1. Thermal Conductivity: Thermal pads generally offer thermal conductivity in the range of 1 to 12 W/m.K, effectively transferring heat from electronic components to heat sinks.
2. Electrical Insulation: Many thermal pads provide excellent electrical insulation, making them suitable for applications requiring electrical isolation.
3. Mechanical Flexibility: The flexibility of thermal pads allows them to conform to uneven surfaces, enhancing thermal contact and reducing air gaps.
4. Durability: Thermal pads are known for their stability over time, maintaining performance without drying out or degrading, even under high temperatures.
Applications
Thermal pads are widely used in electronic devices such as CPUs, GPUs, power transistors, and LED lighting, where they fill the gaps between heat-generating components and heat sinks or metal chassis, ensuring efficient heat transfer.

Understanding Thermal Grease
Composition and Structure
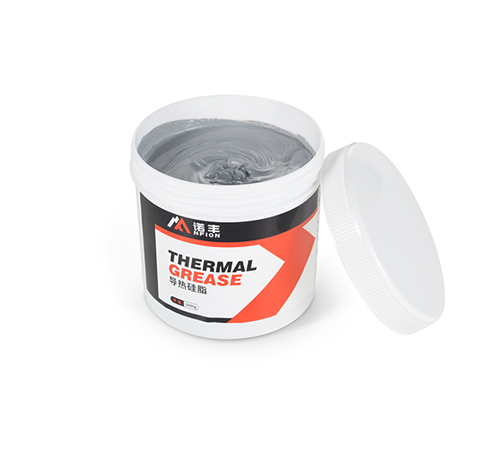
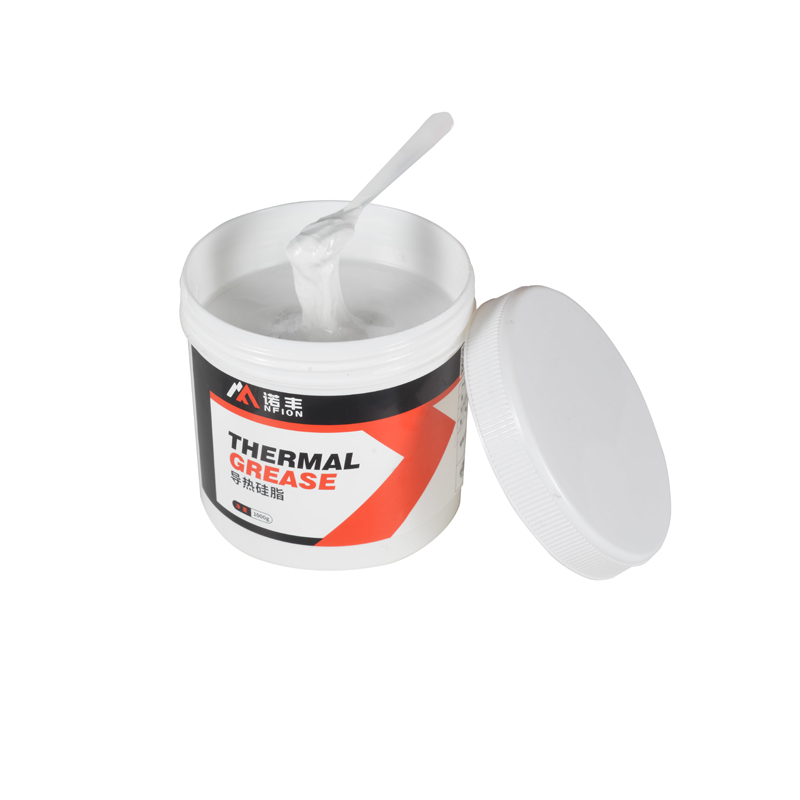
Thermal grease, also known as thermal paste or thermal compound, is a viscous substance composed of silicone oil or other base fluids mixed with thermally conductive fillers like silver, aluminum, or ceramic particles. It is applied as a thin layer between heat-generating components and heat sinks.
Key Characteristics
1. Thermal Conductivity: Thermal grease offers high thermal conductivity, typically ranging from 1 to 8 W/m·K, making it highly effective in transferring heat.
2. Conformability: Due to its paste-like consistency, thermal grease can fill microscopic gaps and surface irregularities, ensuring maximum contact between surfaces.
3. Application and Removal: Applying thermal grease requires precision to ensure an even, thin layer without air bubbles. Removal and reapplication can be messy and time-consuming.
4. Stability: Over time, thermal grease may dry out or pump out (migrate out of the interface), which can reduce its effectiveness and necessitate reapplication.
Applications
Thermal grease is commonly used in high-performance computing environments, such as CPUs, GPUs, and other critical components requiring efficient heat dissipation. It is especially favored in overclocking and other scenarios demanding maximum thermal performance.

Thermal Pad vs. Thermal Grease: Comparative Analysis
Thermal Performance
Both thermal pads and thermal grease provide effective heat transfer, but their performance varies based on the specific application. Thermal grease generally offers slightly better thermal conductivity due to its ability to fill microscopic surface imperfections, resulting in lower thermal resistance. However, thermal pads provide consistent performance over time without the risk of drying out or migrating.
Ease of Application
Thermal pads are easier to handle and apply compared to thermal grease. They can be cut to size and placed directly onto components, requiring minimal preparation. In contrast, applying thermal grease demands precision to avoid excess application or air bubbles, which can compromise thermal performance.
Long-Term Reliability
Thermal pads excel in long-term reliability due to their stable nature. They do not dry out, degrade, or require reapplication, making them ideal for applications where maintenance is challenging. Conversely, thermal grease may need periodic reapplication as it can dry out or pump out over time, especially in environments with significant thermal cycling.
Mechanical and Environmental Considerations
Thermal pads, with their mechanical flexibility, can absorb some mechanical stresses and vibrations, offering better protection in dynamic environments. Thermal grease, while providing excellent thermal performance, does not offer the same level of mechanical stability and may be displaced under mechanical stress.
Conclusion
Choosing between thermal pads and thermal grease depends on the specific requirements of the application. Thermal pads offer ease of use, long-term reliability, and good thermal performance, making them suitable for many consumer electronics and industrial applications. Thermal grease, with its superior thermal conductivity, is ideal for high-performance computing and scenarios where maximum heat dissipation is crucial.
By understanding the properties and applications of both thermal pads and thermal grease, engineers and designers can make informed decisions to optimize thermal management in their devices, ensuring both performance and longevity.


 CN >
CN >