Definition and Composition of Thermal Paste
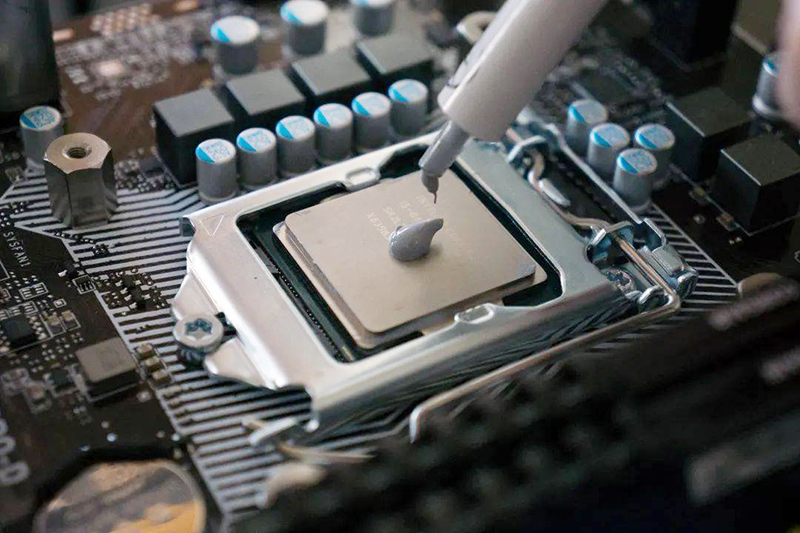
Thermal paste, also known as thermal grease or heat sink compound, is a high-performance thermal conductive material in a paste-like form. It is primarily used to fill microscopic gaps between electronic components and heat sinks, reducing interface thermal resistance and enhancing heat dissipation efficiency. The basic composition of thermal paste typically includes:
1. Base Material (Grease or Oil-based Carrier): Often consists of silicone oil, synthetic esters, or other polymer materials, providing spreadability and ease of application.
2. Thermal Conductive Fillers: Common fillers include aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃), boron nitride (BN), aluminum nitride (AlN), or carbon-based materials such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, enhancing thermal conductivity.
3. Additives: Such as thickeners, antioxidants, and stabilizers, which improve viscosity, temperature resistance, and long-term stability.
Working Principle of Thermal Paste
The contact surfaces between electronic components and heat sinks are not perfectly smooth, creating microscopic air gaps that significantly reduce heat transfer efficiency due to air’s extremely low thermal conductivity (~0.026 W/m·K). Thermal paste works by filling these gaps, achieving the following benefits:
● Increases contact surface area, reducing thermal resistance and improving heat dissipation.
● Optimizes heat transfer pathways, preventing localized overheating.
● Ensures long-term stability, maintaining effective thermal performance over time.
Key Performance Indicators of Thermal Paste
Several critical performance parameters define the effectiveness of thermal paste:
1.Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K): Measures heat transfer efficiency, typically ranging from 1-6 W/m·K.
2.Thermal Resistance (℃·cm²/W): Lower values indicate better heat dissipation efficiency.
3.Operating Temperature Range: Usually from -50°C to 200°C, with high-end products capable of withstanding even higher temperatures.
4.Viscosity and Spreadability: A balanced viscosity ensures easy application without excessive flow.
5.Electrical Insulation: Most thermal pastes are electrically insulating, preventing short circuits, though some metal-filled variants may be conductive.
Applications of Thermal Paste
Thermal paste is widely used across various industries to enhance the thermal management of electronic devices, including:
1. Computers and Servers: Applied to CPUs, GPUs, and Northbridge chips for effective heat dissipation.
2. Consumer Electronics: Used in smartphones, gaming consoles, and routers to maintain optimal temperatures.
3. Automotive Electronics: Essential for electric vehicle control units (ECUs), IGBT modules, and power electronics.
4. LED Lighting: Helps manage heat dissipation in high-power LED systems, increasing efficiency and lifespan.
5. Industrial Equipment and Communication Base Stations: Used in RF modules and power amplifiers to improve reliability.
Selection and Usage Considerations for Thermal Paste
When choosing and applying thermal paste, the following factors should be considered:
1. Select Thermal Conductivity Based on Application: High-power components require pastes with 5 W/m·K or higher.
2. Ensure Long-Term Stability: Avoid products prone to drying out or evaporating, which could degrade performance over time.
3. Apply an Even and Appropriate Thickness: A recommended thickness of 0.1-0.3mm ensures optimal performance; excessive thickness may reduce efficiency.
4. Prevent Contamination and Short Circuits: Some metal-filled thermal pastes can be conductive and should be carefully applied to avoid contact with circuitry.
5. Regular Inspection and Replacement: Over time, thermal paste may dry out, harden, or degrade, necessitating periodic replacement to maintain effective heat dissipation.
Comparison of Thermal Paste with Other Thermal Interface Materials
Thermal paste is one of many thermal interface materials (TIMs). Different TIMs suit different applications:
|
Material Type |
Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
Key Features |
Typical Applications |
|
Thermal Paste |
1-6 |
Easy to apply, adaptable |
Electronics, CPUs, LEDs |
| 1-12 |
Flexible, suitable for large gaps |
Automotive batteries, power modules |
|
|
Thermal Gel |
1-10 |
Combines properties of paste and pads |
Servers, power modules |
|
Thermally Conductive Adhesive |
0.8-2 |
Provides both heat dissipation and bonding |
IGBT, battery bonding |
Conclusion
 CN >
CN >