Do solid-state relays require thermal pads to facilitate heat dissipation?
In electronic systems, solid-state relays (SSRs) are widely embraced for their efficiency, reliability, and extended lifespan in controlling circuits. However, the escalating challenge of heat management has surfaced amidst rising power densities and ambient temperature increases. Among the solutions, thermal pads, as prevalent thermal management materials, have garnered significant interest. This article sets out to explore whether SSRs necessitate the application of thermal pads.
Operating Principles of Solid-State Relays and Heat Dissipation Challenges
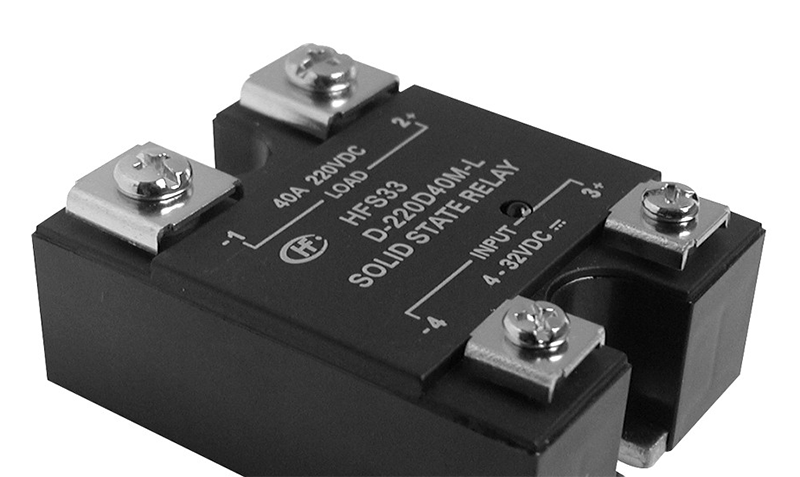
Solid-state relays are semiconductor-based switching devices that leverage components like thyristors or power MOSFETs to govern electrical current flow, thereby facilitating circuit switching. They excel over traditional mechanical relays with attributes such as swift response, longevity, and noiselessness, finding broad application in industrial automation and power systems.
Nonetheless, SSRs produce heat during operation, primarily from conduction losses within the device and switching activities. If this thermal energy isn't efficiently dissipated, it can escalate component temperatures, impairing both performance and longevity. Consequently, proficient heat dissipation design is vital to uphold SSRs' stable functioning.
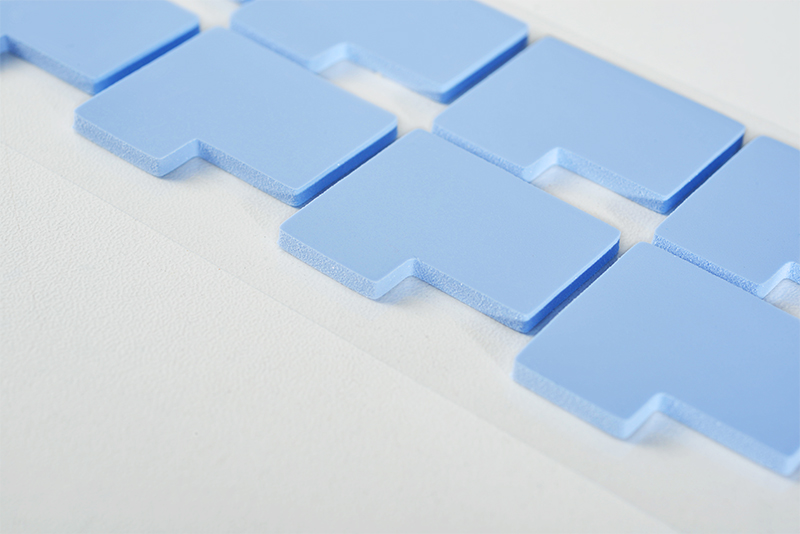

The Function of thermal pads in Solid-State Relays
Heat Transfer Mechanism:
Thermal pads, composed of silicone and thermally conductive fillers, primarily serve to bridge gaps between heat sinks and semiconductor components. By augmenting thermal conductivity, they expedite heat transfer from the device to the heat sink, which subsequently dissipates it into the surroundings, effectively reducing operational temperatures.
Enhanced Cooling Performance:
The implementation of thermal pads dramatically enhances SSR cooling performance. Silicone's inherent suppleness and conformity enable it to seal minuscule gaps between the device and heat sink, minimizing thermal resistance and boosting heat transfer efficiency. This allows SSRs to sustain stable operations even under conditions of high power densities and elevated temperatures.
Protective Function:
In addition to boosting heat dissipation, thermal pads also offer a protective aspect. They alleviate thermal stress concentrations resulting from surface inconsistencies or imperfect installations, thereby reducing thermal stress on components and extending their service life.

Assessing the Need for Thermal Pads in Solid-State Relays
System Power Density and Operating Environment:
Determining whether SSRs require thermal pads hinges initially on the operational environment and the system's power density. For systems with lower power demands and milder ambient temperatures, SSRs might function satisfactorily without supplementary cooling interventions. Conversely, in scenarios marked by high power densities and high temperatures, the inclusion of thermal pads becomes indispensable.
Heat Sink Design and Integration:
Furthermore, the design of the SSR's cooling system influences the requirement for thermal pads. Where heat sinks are meticulously designed to efficaciously conduct and dissipate heat, the inclusion of thermal pads may not be essential. Yet, in compact or enclosed electronic assemblies where cooling is inherently restricted, thermal pads prove crucial.
Cost Considerations:
Lastly, the decision to incorporate thermal pads into SSRs must factor in economic considerations. While these pads are relatively cost-efficient, in straightforward applications where their incremental cooling impact is negligible, omitting them could be a feasible cost-saving measure.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, SSRs operating in environments characterized by high power densities and temperatures necessitate robust cooling strategies to ensure sustained performance. thermal pads, as a proven thermal management solution, contribute to improved SSR cooling efficiency, reduced operating temperatures, and prolonged lifespan. Ultimately, the decision to employ thermal pads in SSRs hinges on a comprehensive evaluation of the specific operating environment, system power demands, the intricacy of heat sink design, and overall cost-effectiveness. In scenarios marked by rigorous power needs, elevated temperatures, or restrictive cooling arrangements, the integration of thermal pads is strongly advocated to safeguard SSR stability and dependability. Conversely, in systems with moderate power requirements, temperate environments, and favorable cooling provisions, the necessity for thermal pads can be weighed against cost-benefit ratios.



 CN >
CN >