What is the Poissons Ratio of Thermal Grease?
Author:NFION
Date:2024-06-24 17:52:55
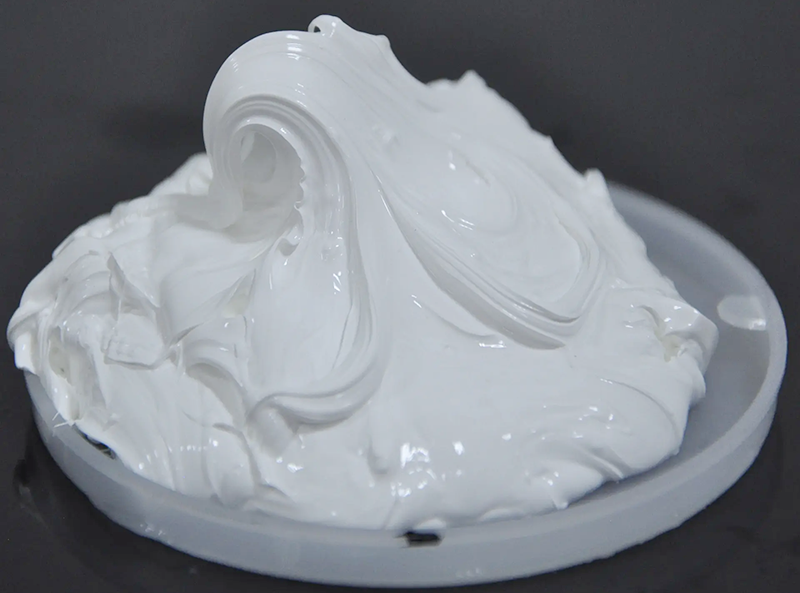

Thermal grease is a common heat dissipation material used in electronic devices, primarily to improve the thermal conductivity between electronic components and heat sinks. To gain a deeper understanding of the performance of thermal grease, the Poisson's ratio is an important physical parameter that merits detailed exploration. This article will provide an in-depth introduction to the Poisson's ratio of thermal grease, its significance, influencing factors, and its impact on applications.
What is Poisson's Ratio?
Poisson's ratio is a critical parameter in material mechanics, defined as the ratio of transverse strain to axial strain when a material is stretched or compressed.
The formula is expressed as:ν= -ϵtransverse / ϵaxia
where ϵtransverse is the transverse strain and ϵaxia is the axial strain. Poisson's ratio reflects the deformation behavior of a material in the perpendicular direction when subjected to a force in one direction.
Poisson's Ratio of Thermal Grease
The Poisson's ratio of thermal grease typically ranges between 0.4 and 0.5. This indicates that thermal grease exhibits significant transverse deformation when compressed. A high Poisson's ratio means that the material tends to expand more easily under pressure, thereby filling more microscopic gaps and enhancing thermal conductivity.
Measurement of Poisson's Ratio
Measuring the Poisson's ratio of thermal grease involves experimental methods such as stress-strain experiments. First, the grease is placed in a specific environment, and a known force is applied to observe its deformation. Then, using strain gauges and other equipment, the transverse and axial strains are measured, allowing for the calculation of Poisson's ratio.
Significance of Poisson's Ratio
Thermal Performance
Poisson's ratio directly impacts the thermal performance of thermal grease. A higher Poisson's ratio enables the grease to better fill the microscopic gaps on the contact surface, reducing thermal resistance and thereby improving thermal efficiency. This is especially crucial for the heat dissipation of high-power electronic devices.
Mechanical Performance
Poisson's ratio also affects the mechanical performance of thermal grease. A high Poisson's ratio means that the material will produce more significant transverse deformation when compressed, which in some applications might lead to the material being squeezed out from the contact surface, thus affecting thermal performance. Therefore, when selecting thermal grease, its Poisson's ratio must be considered in conjunction with the specific application requirements.
Factors Affecting Poisson's Ratio
Formulation and Composition
The formulation and composition of thermal grease significantly influence its Poisson's ratio. The type and proportion of thermally conductive particles and the base material in the grease can alter its mechanical properties. For example, increasing the content of thermally conductive particles might enhance thermal performance but also change the flexibility and Poisson's ratio of the material.
Temperature
Temperature also affects the Poisson's ratio of thermal grease. Typically, as the temperature increases, thermal grease becomes softer, potentially changing its Poisson's ratio. Therefore, for thermal grease used in high-temperature environments, special attention must be paid to how its Poisson's ratio varies with temperature.
Considerations in Applications
In practical applications, selecting thermal grease with an appropriate Poisson's ratio is crucial. For electronic devices requiring high thermal performance and smooth contact surfaces, grease with a higher Poisson's ratio should be chosen to ensure adequate filling of the contact surface. However, for applications with significant mechanical stress or requiring high mechanical strength, grease with a moderate Poisson's ratio should be selected to prevent the material from being squeezed out.
Conclusion
The Poisson's ratio of thermal grease is a key parameter that directly affects its thermal and mechanical performance. Understanding the concept of Poisson's ratio, its measurement methods, and influencing factors is essential for selecting and applying the appropriate thermal grease. By comprehensively considering the Poisson's ratio of thermal grease and its behavior under different temperatures and pressures, the thermal design of electronic devices can be optimized, enhancing their performance and reliability.
 CN >
CN >