Network switches are crucial hardware devices in modern data centers and enterprise networks, handling high-intensity data exchange tasks. Due to their prolonged, high-load operation, temperature control is essential to ensure their stability, performance, and lifespan. Overheating can lead to performance degradation, system crashes, and even permanent damage to the equipment. NFION explores effective measures to prevent network switches from overheating and provides a series of practical solutions.

The Dangers of Network Switch Overheating
1. Performance Degradation
When a network switch overheats, the performance of its internal electronic components is compromised, causing slower data transfer speeds, higher packet loss rates, and other issues.
2. Shortened Lifespan
High temperatures accelerate the aging of electronic components, reducing the lifespan of the device. Network switches operating under prolonged high temperatures may experience frequent failures, leading to increased maintenance costs.
3. Network Failures
Overheating can cause the device to malfunction, resulting in network interruptions and data loss. These disruptions can severely impact business operations and user experience.
Causes of Overheating in Network Switches
Before exploring preventive measures, it is essential to understand the primary factors that lead to overheating:
1. Excessive Load
When a network switch handles excessive data traffic or processes numerous packets simultaneously, it generates significant heat, causing the temperature to rise. High-density switches or those operating under high bandwidth are particularly prone to heat buildup.
2. Insufficient Ventilation
Network switches are often installed in racks or enclosures. Poor ventilation or inefficient cooling systems can trap hot air, leading to overheating.
3. Hardware Failures
Faulty fans, detached heat sinks, or aging components may compromise the switch’s cooling capabilities, resulting in high temperatures.
4. Environmental Factors
A hot ambient environment exacerbates the cooling challenges. In high-temperature conditions, natural heat dissipation becomes less effective.

Effective Measures to Prevent Overheating
Preventing overheating in network switches involves addressing hardware design, environmental management, and operational maintenance.
1. Optimize Device Configuration and Load Distribution
● Load Balancing: Use load balancers to distribute traffic across multiple switches, reducing the pressure on individual devices.
● Dynamic Bandwidth Adjustment: Adjust bandwidth dynamically based on real-time traffic demands to mitigate peak loads.
● Performance Monitoring: Regularly monitor the switch’s performance and load to identify and address anomalies promptly.
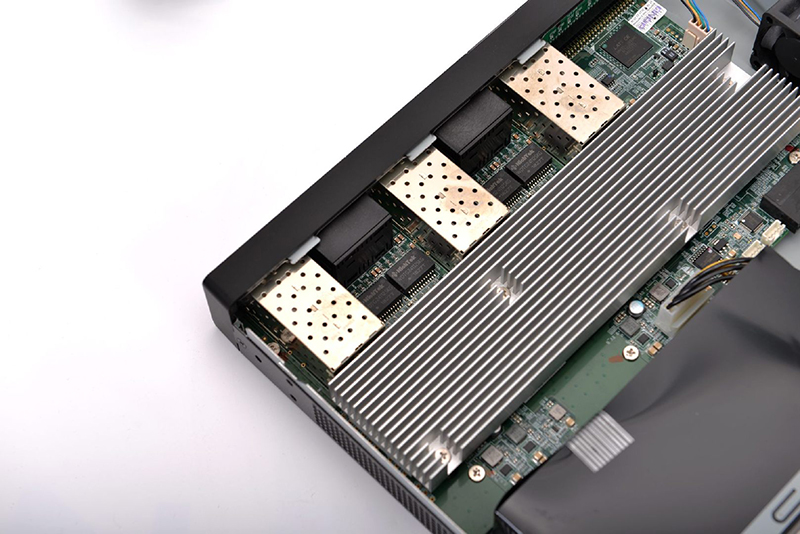
2. Enhance Cooling Design
● Fan Configuration: Ensure that built-in fans function correctly. Select appropriate fan numbers and power levels based on the device model and application scenario. Regularly clean and maintain fans to prevent dust accumulation.
● Heat Sink Design: Install heat sinks on critical components to increase the heat dissipation area and accelerate heat transfer.
● Liquid Cooling Systems: For high-performance switches, especially in large-scale data centers, consider liquid cooling technology, which leverages coolant for efficient thermal management.
3. Optimize Installation Environment
● Well-Ventilated Server Rooms: Choose server rooms with proper ventilation and controlled temperatures. Avoid placing switches in poorly ventilated or sunlit areas.
● Air Conditioning and Environmental Monitoring: Install efficient air conditioning systems in server rooms and perform regular maintenance. Use environmental monitoring tools to track room temperature and humidity in real time.
● Temperature Sensors and Alarm Systems: Install temperature sensors around switches to monitor device temperatures. Configure alarm thresholds to alert administrators if temperatures exceed safe levels.
4. Routine Maintenance and Cleaning
● Clean Fans and Heat Sinks: Regularly clean the interior of switches, especially fans and heat sinks, to prevent dust from reducing cooling efficiency.
● Check Hardware for Faults: Periodically inspect fans, power supplies, and cooling components to ensure they function correctly. Replace or repair faulty parts promptly.
5. Utilize Efficient Thermal Management Materials
● Thermal Interface Materials: Apply high-conductivity materials (e.g., thermal conductive pads, thermal gels) to critical components to enhance heat transfer efficiency.
● Optimized Thermal Design: For high-power devices, refine the thermal design by adding heat dissipation pathways or improving heat sink structures.
Conclusion
Overheating in network switches significantly impacts device performance and stability. Preventing this issue requires a multifaceted approach, including load optimization, improved cooling design, environmental control, and regular maintenance. Additionally, employing advanced thermal management materials is an essential solution to thermal challenges. By implementing these measures, network switches can maintain optimal performance and stability even under high-load, long-term operations, thereby enhancing overall network efficiency.



 CN >
CN >