In modern electronic device design and manufacturing, thermal management is a critical consideration. As the performance of electronic components improves, so does their heat generation, making efficient heat dissipation essential for ensuring device stability. Thermal conductive materials, such as thermal conductive pads and thermal grease, are widely used in electronic devices due to their excellent thermal properties. However, these two materials exhibit significant differences in characteristics, application scenarios, and performance. NFION will explore the differences between thermal conductive pads and thermal grease in detail to help engineers and technical personnel make more informed decisions.
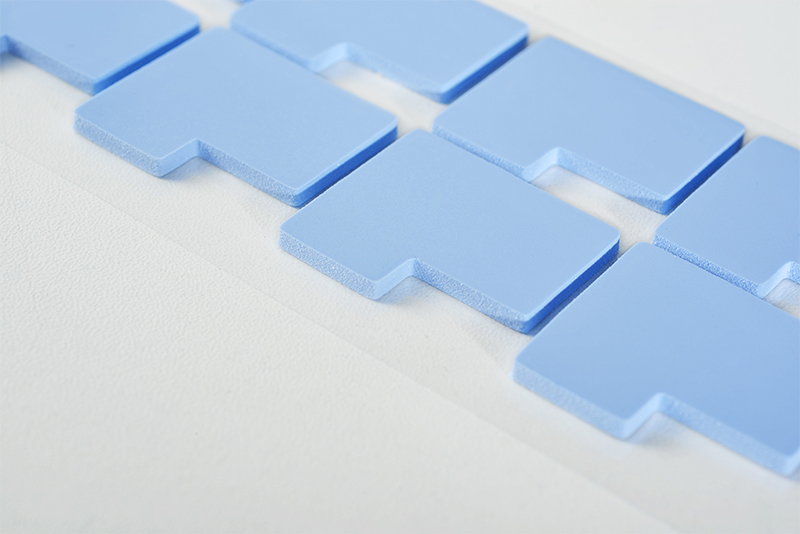

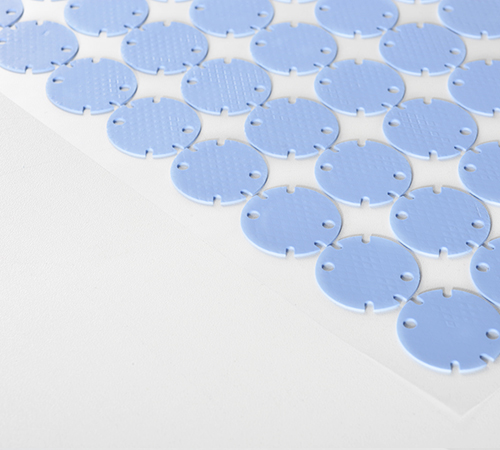
Thermal Conductive Pads
1.1 Definition and Composition
Thermal conductive pads are sheet-like materials made from silicone rubber mixed with thermal fillers. The main components include silicone resin, thermal fillers (such as aluminum oxide, zinc oxide, etc.), and other additives. This material usually comes in sheet, pad, or custom shapes.
1.2 Characteristics
- High Thermal Conductivity: The thermal conductivity of thermal conductive pads typically ranges from 1.0-12.0 W/m.K, effectively transferring heat.
- Electrical Insulation: Most thermal conductive pads have good electrical insulation properties, making them suitable for applications requiring electrical insulation.
- Flexibility: With a certain degree of softness and elasticity, they can conform well to uneven surfaces and fill gaps.
- Stability: Resistant to high temperatures and corrosion, with a long service life.
1.3 Application Scenarios
Thermal conductive pads are widely used in scenarios requiring stable and reliable heat dissipation, such as:
- Heat transfer between electronic components, like between a CPU and a heatsink.
- Thermal management in LED lighting devices.
- Thermal management in power supply equipment.
- High-efficiency heat dissipation in communication equipment and medical devices.
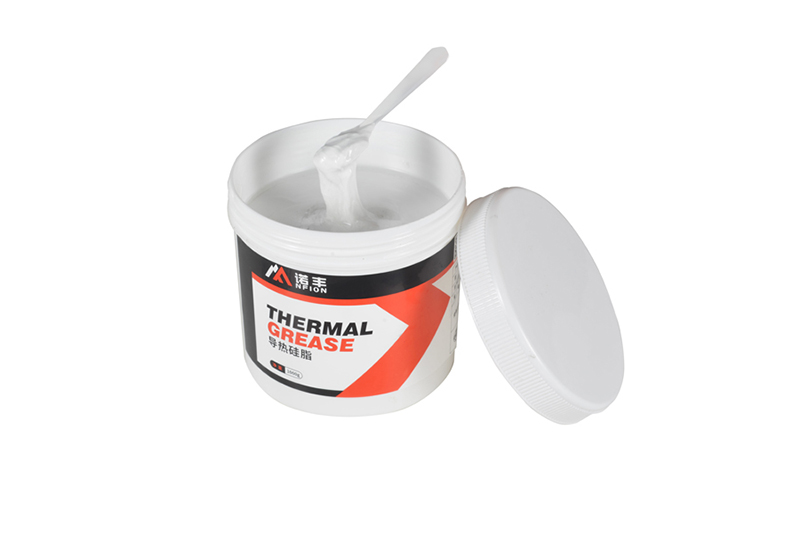

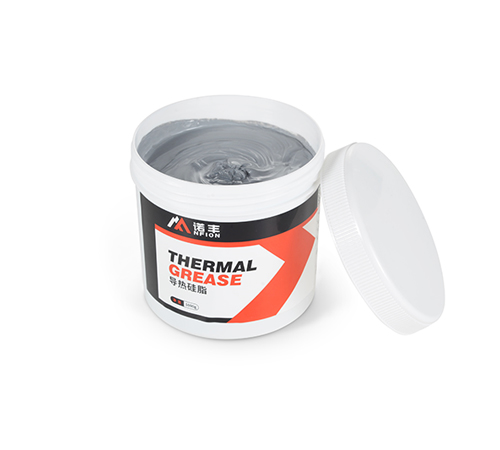
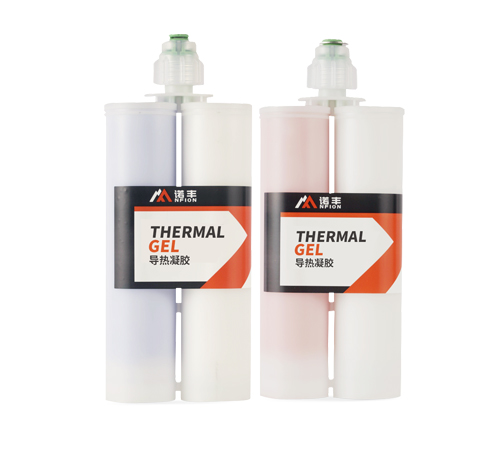
Thermal Grease
2.1 Definition and Composition
Thermal grease, also known as thermal paste or thermal compound, is a paste-like material formed by mixing silicone oil with thermal fillers. The main components are silicone oil, thermal fillers, and thickeners.
2.2 Characteristics
- High Thermal Conductivity: The thermal conductivity of thermal grease generally ranges from 1.0-5.0 W/m·K, effectively conducting heat.
- Low Thermal Resistance: It can fill microscopic uneven surfaces, improving the thermal transfer efficiency of contact surfaces.
- Flexible Application: Due to its paste-like nature, thermal grease can be applied flexibly to contact surfaces of various shapes and sizes.
- Ease of Use: It can be applied through brushing, dispensing, and other methods.
2.3 Application Scenarios
Thermal grease is typically used in scenarios requiring flexible application and high thermal conductivity, such as:
- Heat dissipation of CPUs and GPUs.
- Heat transfer between power transistors and heatsinks.
- Thermal management in small electronic devices.
- Heat dissipation needs with special shapes or requiring flexible handling.

Comparison of Thermal Conductive Pads and Thermal Grease
3.1 Thermal Performance
Both thermal conductive pads and thermal grease have good thermal performance, but they differ in specific applications. Thermal conductive pads usually have higher thermal conductivity, suitable for scenarios requiring efficient heat transfer; while thermal grease, due to its paste-like nature, can better fill tiny gaps, improving thermal transfer efficiency.
3.2 Installation and Use
The installation of thermal conductive pads is relatively simple; they only need to be cut and adhered to the required areas, making them suitable for mass production and standardized manufacturing. Thermal grease requires smearing or dispensing, which, although more flexible, requires certain operational skills, making it suitable for scenarios requiring customized handling.
3.3 Long-term Stability
Thermal conductive pads have good long-term stability, not easily degrading or drying out, suitable for long-term fixed heat dissipation needs. Thermal grease may dry out or degrade over time, requiring periodic replacement or maintenance.
3.4 Cost Consideration
Due to production processes and material properties, thermal conductive pads are relatively expensive but have a long service life, suitable for long-term investment. Thermal grease is relatively low-cost, suitable for short-term or medium-term applications.
Conclusion
As crucial materials in the thermal management of electronic devices, thermal conductive pads and thermal grease each have their unique advantages and suitable application scenarios. When choosing between them, one must consider thermal performance, installation methods, long-term stability, and cost. Thermal conductive pads are suitable for scenarios requiring efficient and stable heat dissipation, while thermal grease is ideal for flexible applications and customized heat dissipation needs. By selecting the appropriate thermal material, the thermal efficiency and overall performance of electronic devices can be significantly improved.


 CN >
CN >